일반화선형회귀 : boston housing 집값 예측하기
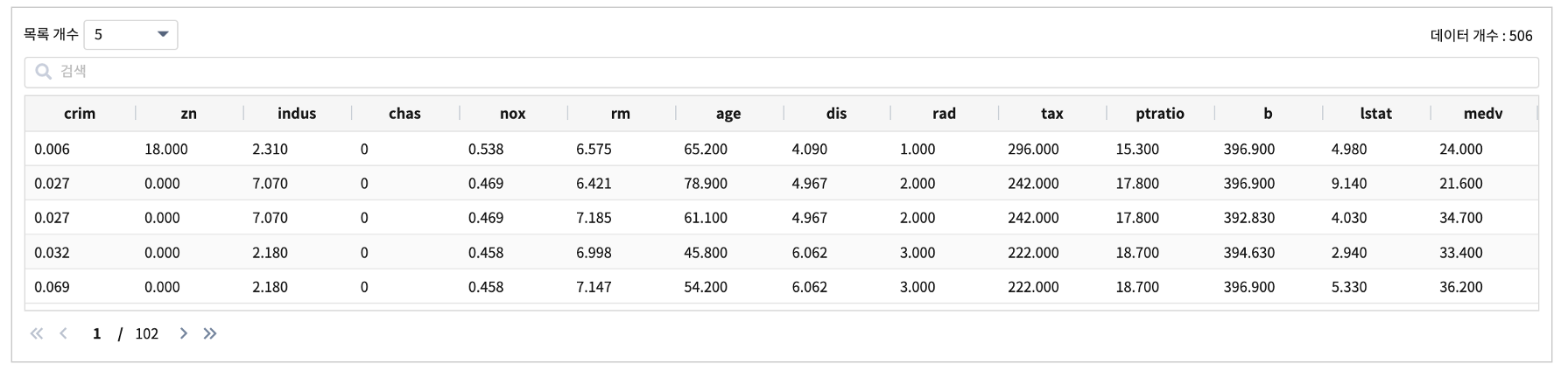
keras 의 dataset 중 하나인 boston housing 데이터는 보스턴 시의 주택 가격에 대한 데이터로 여러 개의 측정지표들 (예를 들어, 범죄율, 학생/교사 비율 등) 13개를 독립변수로 포함하고, 보스턴 인근의 주택 가격의 중앙값(median value) 1개를 종속변수로 하여 총 14개의 변수로 구성 되어 있습니다.
일반화선형회귀(Generalized Linear Regression) 알고리즘으로 학습 모델을 생성하여 주택 가격을 예측해 봅니다.
일반화선형회귀(Generalized Linear Regression)
선형회귀 모델은 종속변수의 분포가 정규분포라고 가정합니다. 일반화 선형 모델(generalized linear regression)은 선형회귀 모델을 확장하여 종속변수의 분포를 정규 분포외에 다른 확률분포(이항분포, 포아송 분포 등)도 고려하여 만든 모델입니다. 종속변수의 family 분포(gaussian, binomial, poisson, gamma and tweedie) 는 데이터의 특성을 파악한 사용자가 결정하여 파라미터로 모델링에 적용합니다.
데이터 전처리(preprocessing)
데이터 출처 keras data set
IRIS 에 데이터모델
EDU_ML_boston_house로 생성합니다.
필드 설명
feature |
description |
crim |
자치시(town)별 1인당 범죄율 |
zn |
25,000 평방 피트를 초과하는 거주지역의 비율 |
indus |
비소매상업지역이 차지하고 있는 토지의 비율 |
chas |
찰스강의 경계에 위치한 경우는 1, 아니면 0 |
nox |
10ppm 당 농축 일산화질소 |
rm |
주택 1가구당 평균 방의 수 |
age |
1940년 이전에 건축한 소유주택 비율 |
dis |
보스톤 직업센터까지의 접근성 지수 |
rad |
방사형 도로까지의 접근성 지수 |
tax |
10,000 달러당 재산세율 |
ptratio |
자치시(town)별 학생/교사 비율 |
b |
자치시(town)별 흑인의 비율 |
lstat |
모집단의 하위 계층의 비율 |
medv |
본인 소유의 주택가격 중앙값(단위 $1000) |
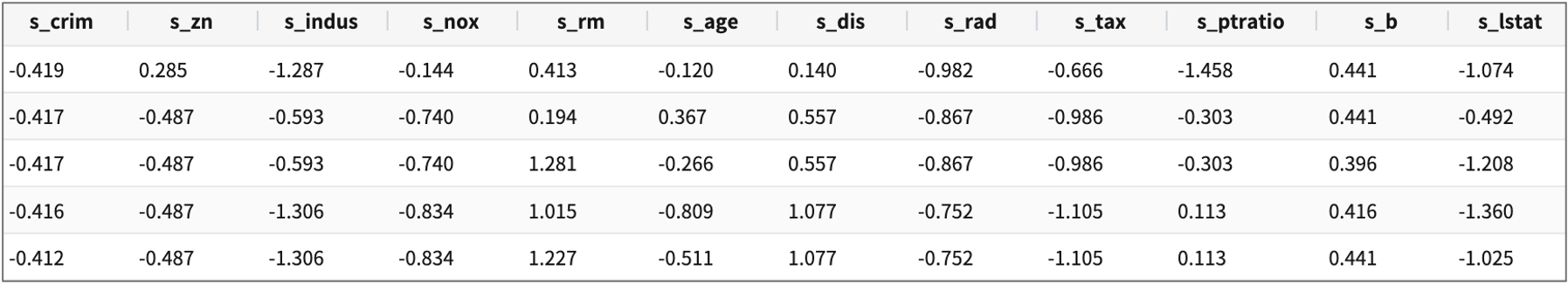
13개 변수중 범주형변수 chas ( 강의 경계일 때는 1, 아닐 때는 0) 를 제외하고, 각각의 변수들은 측정값의 단위가 다르기 때문에 스케일링이 필요합니다.
chas 를 제외한 feature 변수 12개에 standard scaling 을 적용하고
s_기존변수이름으로 생성합니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
1차 학습 모델 생성 (fit)
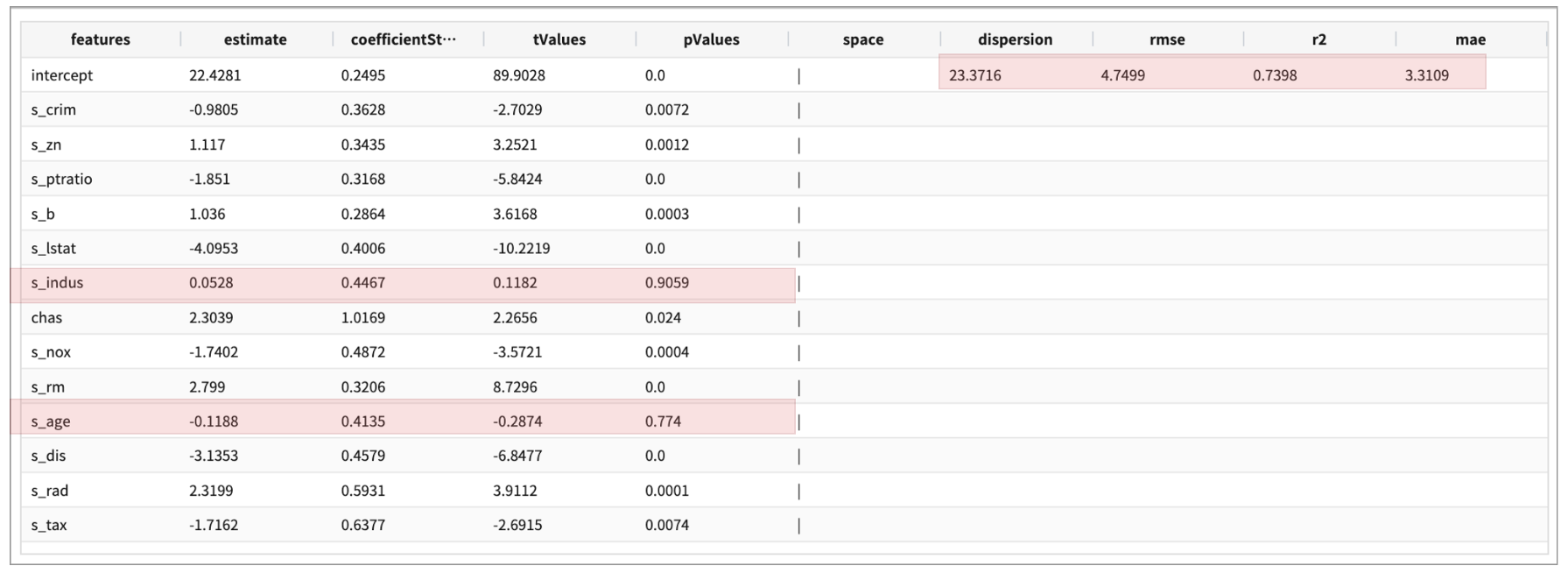
1차 모델은 scaling한 변수12개, 범주형 변수 chas => 설명 변수(X) 13개 전체로 GeneralizedLinearRegression 알고리즘의 예측모델을 생성합니다.
데이터모델 EDU_ML_boston_house 의 80% 를 random sampling 하여 training data 로 삼아 학습을 진행합니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.8
| fit GeneralizedLinearRegression FEATURES s_crim, s_zn, s_indus, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_age, s_dis, s_rad, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
LABEL medv maxIter=30 regParam=0.1 fitIntercept=True solver=irls
첫번째 fit 결과
2차 학습 모델 생성 (fit)
두번째 학습 모델에서는 첫번째 fit 결과에서 pValues 가 0.05 보다 큰 s_age, s_indus 를 빼고 11개 설명변수로 예측모델을 생성합니다.
.. | fit generalizedlinearregression FEATURES s_crim, s_zn, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_dis, s_rad, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
LABEL medv maxIter=30 regParam=0.1 fitIntercept=True solver=irls INTO GLM_house_model_02
두번째 fit 결과
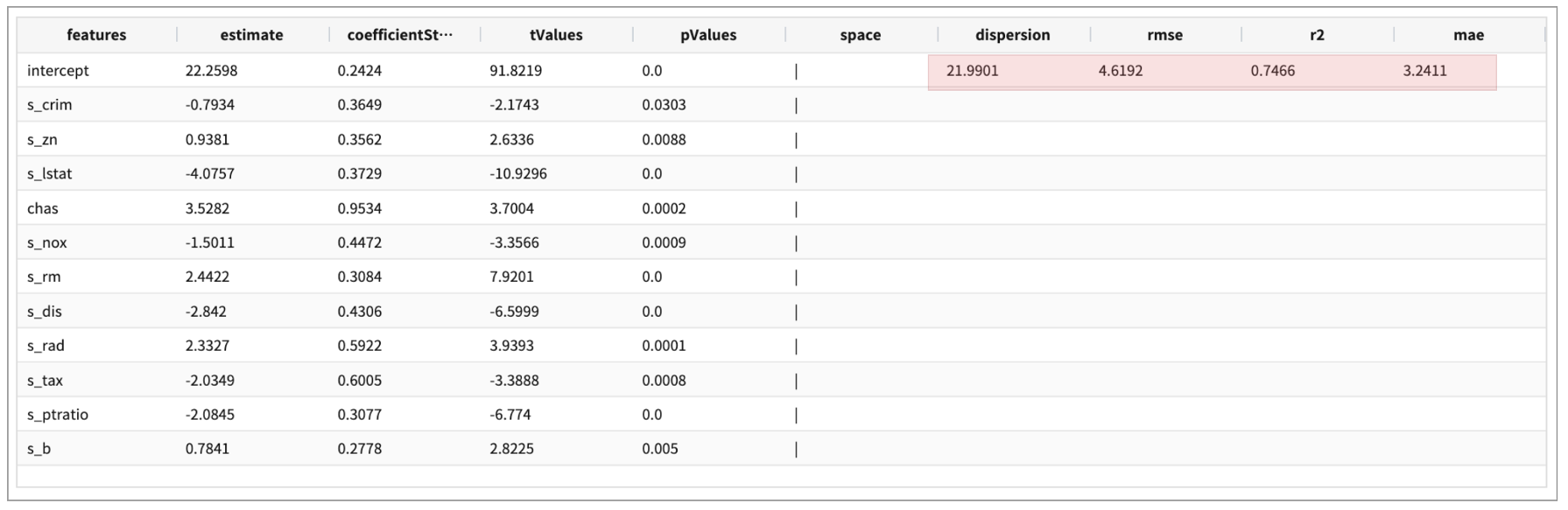
13개 변수 전체로 만든 1차 모델보다 11개 변수로 만든 두번째 모델의 RMSE(RootMeanSquaredError) 가 더 작습니다. (4.7499 -> 4.6192) 따라서 두번째 모델 “GLM_house_model_02” 으로 예측값을 구해 봅니다.
테스트 데이터로 예측하기 (predict)
11개 설명변수로 생성한 두번째 학습 모델 “GLM_house_model_02” 로 test 데이터를 대상으로 주택가격(medv)을 예측합니다. 테스트 데이터 역시 training 데이터에서 사용한 standard scaling 을 그대로 사용하여 정규화 한 후 예측에 사용합니다.
아래 검색어는 전체 데이터에 스케일링 적용 후 20% 의 데이터를 random sampling 하여 테스트데이터로 삼아서 예측할 때의 검색어입니다.
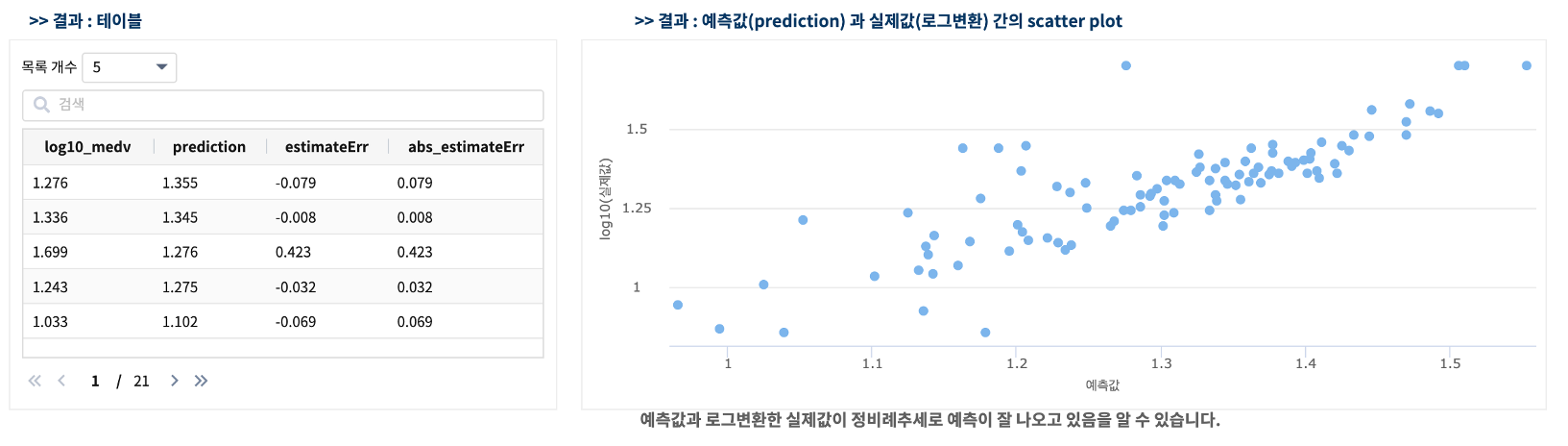
예측값 prediction 과 실제값 medv 의 차이를 계산하여 예측오차 까지 구해 봅니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.2
| fields s_crim, s_zn, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_dis, s_rad, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat,medv
| predict demo.GLM_house_model_02 s_crim, s_zn, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_dis, s_rad, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
| fields medv, prediction
| calculate medv - prediction as estimateErr
실행 결과
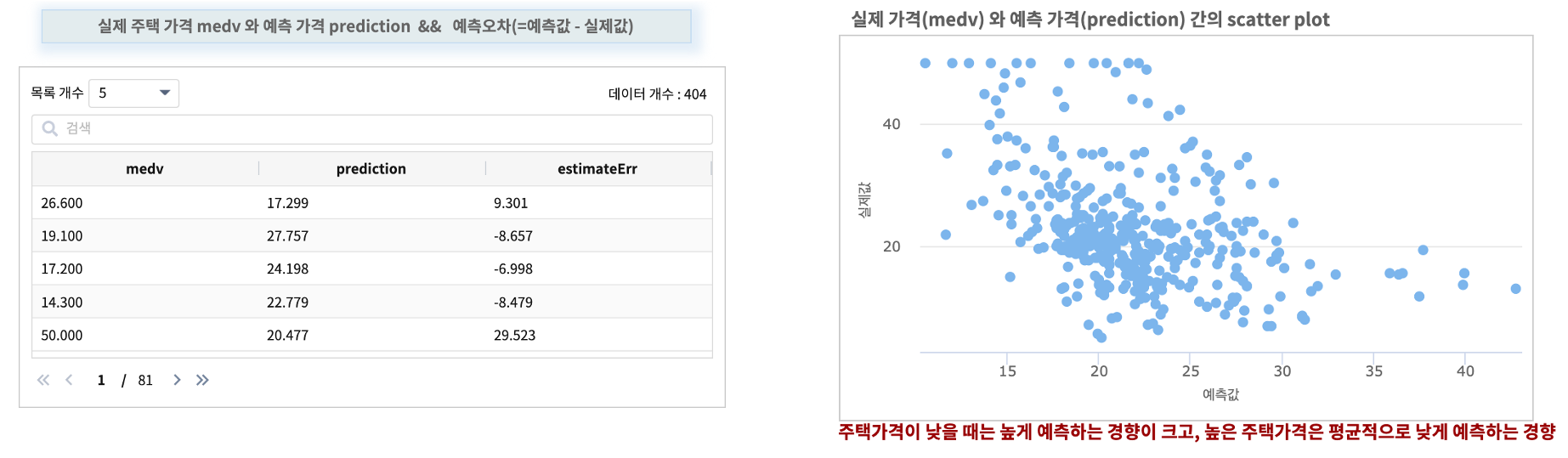
예측오차는 주택가격이 고가일수록 예측 오차가 증가하는 것으로 보입니다.
즉 종속변수(Y)인 주택가격(medv) 역시 변환이 필요합니다.!!! => 로그변환필요
데이터 전처리 프로세스에 주택가격 로그변환 추가
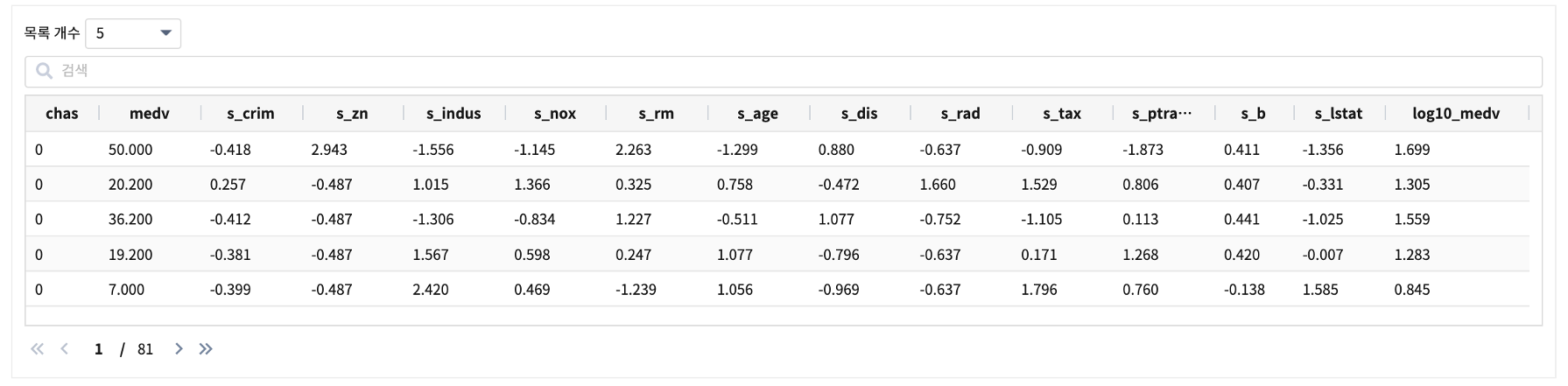
기존 13개 feature 변수를 standard scaling 변환 + medv 변수의 로그 변환(log10_medv)
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.8
| sql "select *, log(10, medv) as log10_medv from angora"
결과
3차 학습 모델 생성(fit)
3차 학습 모델 생성은 정규화 변환한 13개 feature 변수와 로그변환한 medv 변수를 대상으로 학습을 실행합니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.8
| sql "select *, log(10, medv) as log10_medv from angora"
| fit GeneralizedLinearRegression FEATURES s_crim, s_zn, s_indus, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_age, s_dis, s_rad, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
LABEL log10_medv maxIter=30 regParam=0.1 fitIntercept=True solver=irls
결과
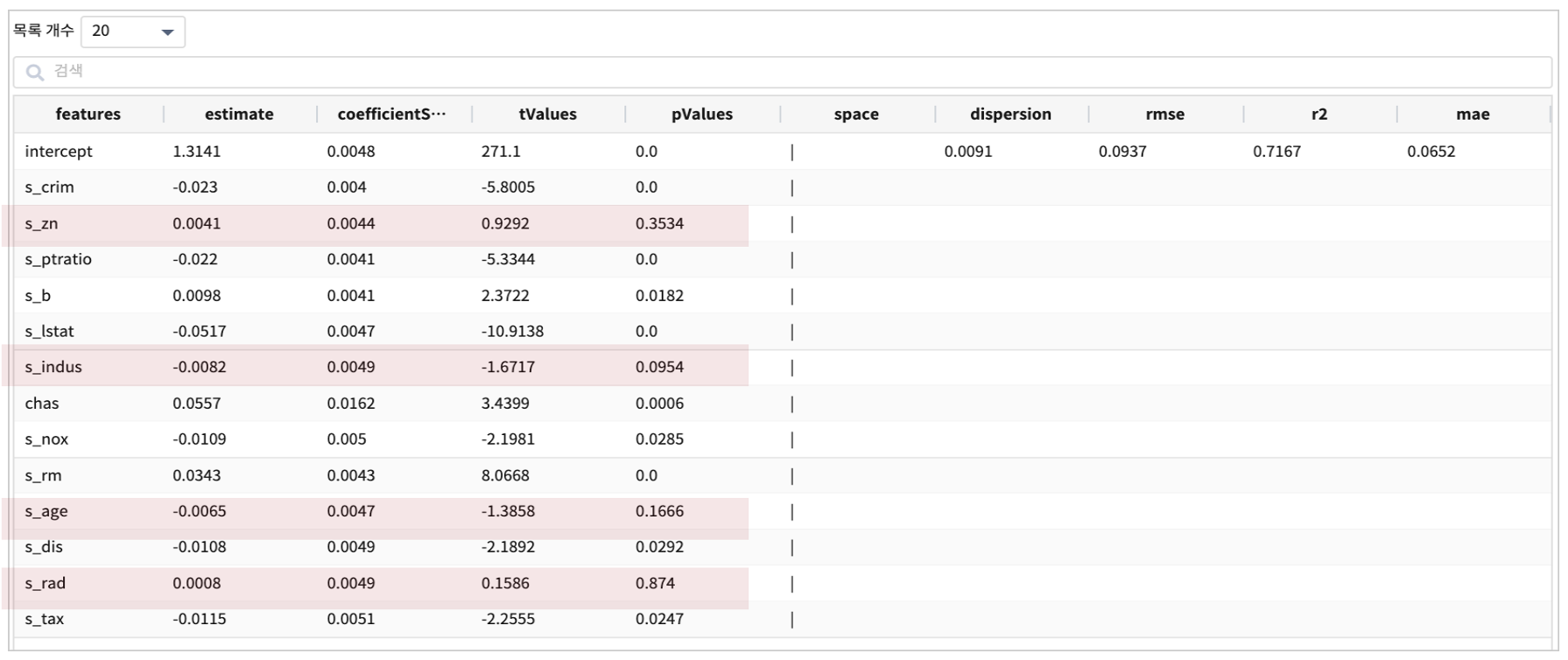
pValues 가 0.05 보다 작은 s_zn, s_indus, s_age, s_rad 를 FEATURE에서 제외해서 다시 모델링을 해봅니다.
4차 학습 모델 생성(fit)
4차 학습 모델 생성은 s_zn, s_indus, s_age, s_rad 를 제외한 9개 feature 변수와 로그변환한 medv 변수를 대상으로 학습을 실행합니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.8
| sql "select *, log(10, medv) as log10_medv from angora"
| fit GeneralizedLinearRegression FEATURES s_crim, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_dis, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
LABEL log10_medv maxIter=30 regParam=0.1 fitIntercept=True solver=irls INTO GLM_house_model_log_03
결과
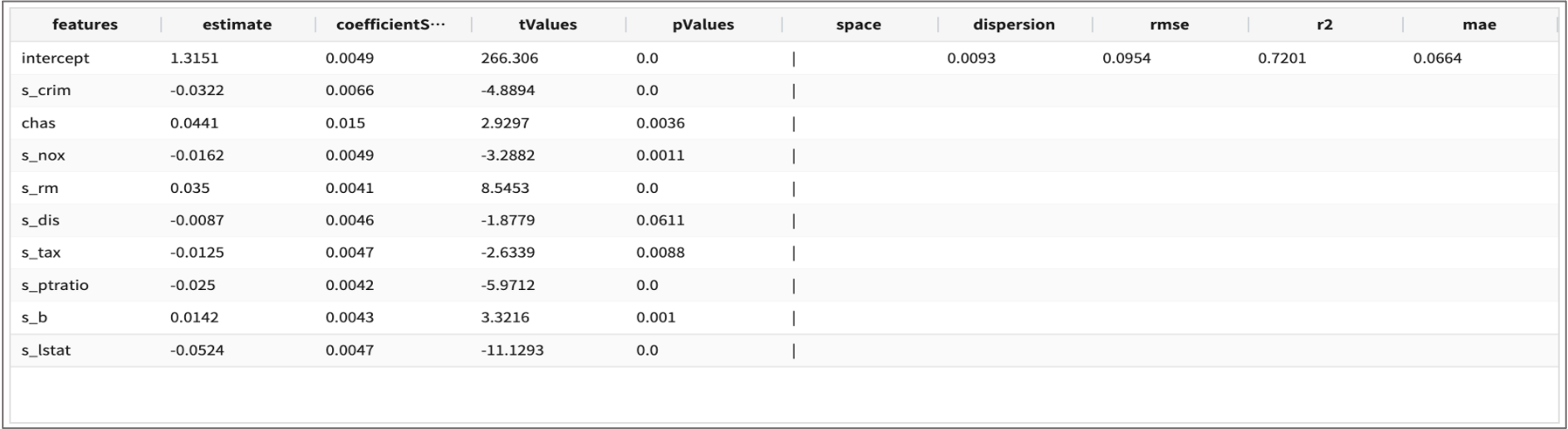
GLM_house_model_log_03 을 에측 모델로 선택합니다.테스트 데이터로 예측하기 (predict GLM_house_model_log_03)
9개 feature 설명변수, 로그 변환한 medv 로 생성한 네번째 학습 모델 “GLM_house_model_03” 로 주택가격(medv)을 예측합니다. 테스트 데이터 역시 training 데이터에서 사용한 standard scaling 을 그대로 사용하여 정규화 한 후 예측에 사용합니다.
* | scaler standard crim to s_crim, zn to s_zn, indus to s_indus, nox to s_nox, rm to s_rm, age to s_age, dis to s_dis, rad to s_rad, tax to s_tax, ptratio to s_ptratio, b to s_b, lstat to s_lstat
| sampling RATIO 0.2
| sql "select *, log(10, medv) as log10_medv from angora"
| predict demo.GLM_house_model_log_03 s_crim, chas, s_nox, s_rm, s_dis, s_tax, s_ptratio, s_b, s_lstat
| fields log10_medv, prediction
| sql "select *, (log10_medv - prediction ) as estimateErr, sqrt(log10_medv - prediction ) as sqrt_estimateErr from angora"
결과